In theory, convertible stem designs allow for stem retention during revision from anatomical to reverse
shoulder arthroplasty. In some cases stem retention is not possible because of excessive soft tissue tensioning, infection, fracture, stem loosening or malpositioning (too high, too low, malrotation).
These authors reviewed 2834 arthroplasties from the Dutch Arthroplasty Registry comparing convertible and non-convertible stems.
Mean follow-up for the convertible design prostheses was 2.1 years and 2.5 years for the non-convertible prostheses (p < 0.01).
6.7% (71/1067) of the convertible prostheses had a revision, or 3.2%/year of followup
4.5% (65/1430) of the non-convertible prostheses had a revision, or 1.8%/year of followup
4.6% (50/1067) of the convertible prostheses were revised to reverse total shoulder
2.2% (31/1430) of the non-convertible prostheses were revised to a reverse total shoulder
42% of the convertible prostheses revised to reverse total shoulder required stem revision
90% of the non-convertible prostheses revised to reverse total shoulder required stem revision
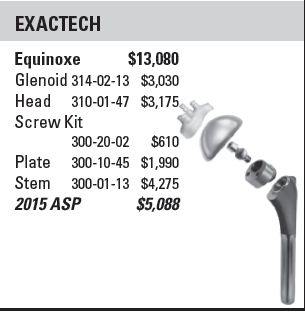
Comment: The relative costs of the convertible and non-convertible prostheses are not presented in this paper. Dermining the value of the convertible stem requires consideration of the revision rate/year and the cost of the implant. Convertible stems may be of greatest value in the subset of arthroplasties at high risk for revision to a reverse total shoulder.
Here is another article related to our topic:
Conversion to Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty with and without Humeral Stem Retention:The Role of a Convertible-Platform Stem
These authors retrospectively reviewed 102 shoulders having revision of an anatomic shoulder arthroplasty to a reverse total shoulder. 73 of the shoulders had exchange of the humeral stem and 29 had retention of a convertible-platform humeral component stem.
The authors conclude that shoulder arthroplasty systems utilizing a convertible-platform humeral stem offer an advantage when conversion to a reverse total shoulder is performed, provided that the stem is well-fixed and in proper position.
While the authors state that "the cost of a modular platform stem is, on average, similar to the cost of a modular non platform stem", cost data is not presented. If the argument is that all anatomic arthroplasties should be performed with platform stems, even a small cost differential could have a major impact on the expenditures for shoulder joint replacement. Looking at the reference listed in the article we see that some convertible stems require adapters to mate the stem with the humeral head.



An anatomic arthroplasty can fail for many reasons, including malposition, instability, delayed cuff failure and pseudo paralysis. In these situations consideration can be given to conversion of the anatomic prosthesis to a reverse total shoulder as shown here. As demonstrated in that post out preferred method for managing a failed anatomic arthroplasty is to completely remove the existing implant, obtain cultures, and then implant the reverse prosthesis. This approach allows full access to the glenoid and optimal positioning of the humeral component of the reverse. Removal of the anatomic implant is almost always possible and is particularly straightforward if it was inserted using impaction grafting.
In certain cases, such as that shown here, a well fixed stem can be retained and the proximal end converted to a reverse total shoulder with insertion of a glenosphere. Here's another post regarding conversion with retention of the anatomic stem.
Recently, there has been the advent of 'platform' prostheses, in which a humeral stem is fixed in the humeral canal that can be attached to either an anatomic or a reverse proximal humeral prosthesis. For examples, see here, here, here, and here.
It is important to recognize that in a reverse, (1) the glenosphere is placed inferiorly on the glenoid face, (2) the proximal humeral part of the reverse is bigger than that of an anatomic humeral arthroplasty and (3) the soft tissue tensioning considerations of a reverse are different from those of an anatomic arthroplasty. Therefore, the proximal-distal positioning of the humeral component needs to be fine tuned to achieve the ideal reverse arthroplasty. While some systems provide various adaptors to adjust the height, inclination and version of the proximal humeral prosthesis, the flexibility in positioning is limited by the use of the 'platform' fixed in the humeral canal.
Fortunately, we now have a clearer understanding of the indications for a reverse total shoulder, so that the needs for convertible prostheses is diminishing. For example, it is becoming evident that proximal humeral fractures in elderly individuals are often best managed by a primary reverse total shoulder - the idea of 'trying' an anatomic arthroplasty that is convertible to a reverse later is not so appealing. Similarly, individuals with arthritis, cuff deficiency, and instability are also best managed by a primary reverse.
See related post here.
One of the aspects lacking in articles about platform and other types of new shoulder prostheses is the incremental cost of the implant. This information is necessary to determine the value (benefit/cost) of the device. The question becomes, for 100 anatomic arthroplasties, how many successful conversions to reverses would be necessary to justify the incremental cost of (1) the implant and (2) the learning curve?
In our practice, revision of an anatomic to a reverse prosthesis is required almost exclusively in cases where the index procedure is done elsewhere. Often there are problems with stem fixation or positioning that require stem removal, even if 'in theory' the platform stem is convertible to a reverse.
One of the advantages of fixation of a humeral stem with impaction grafting is that - should conversion to a reverse prosthesis be required - the stem can be easily removed and the reverse stem inserted at the desired height and version.
Finally, infection with Propionibacterium is now recognized as a not unusual complication of shoulder arthroplasty. A well fixed stem for a platform prosthesis makes prosthesis exchange complicated.
Future studies will be helpful in determining the cost effectiveness of convertibles in shoulder arthroplasty.